Prosthetics is the branch of dentistry concerned with replacing one or more teeth in order to ensure correct oral function and aesthetic appearance.
Partially damaged teeth can be restored by means of full crowns, inlays, or veneers.
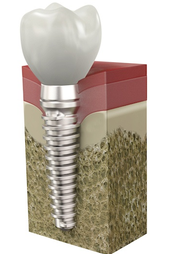
Missing teeth can be replaced by means of implants, bridges, or removable prostheses.
If several teeth are missing, they can be replaced by means of bridges, multiple implants, or removable prostheses.
If all the teeth are missing, they can be replaced by means of a complete prosthesis, commonly known as “dentures”, or prosthesis on implants.
Crowns are a type of prosthetic restoration which completely caps the visible portion of a tooth.
They are bonded directly to the tooth and cannot be removed by the patient.
The use of crowns is advisable in the case of teeth which are at high risk of fracture (in this case, the purpose of crowns is to protect the teeth from masticatory loads), or teeth with extensive destruction of the crown, so that conservative restoration with veneers or inlays is no longer possible.
Crowns can be made of gold-resin, metal-ceramic, zirconia-ceramic, or full ceramic.
Veneers are thin ceramic or composite layers bonded to the external surface of a tooth to improve its appearance.
This technique involves reducing the external portion of the tooth.
Veneers are commonly used in the following situations:
-
overly pigmented teeth on which standard whitening treatments are inappropriate;
-
gaps between the teeth which the patient wishes to close;
-
teeth of abnormal shape;
-
fractured teeth: in these cases, the veneer replicates the exterior shape and the missing portion of the tooth.
Inlays are indirect fillings of teeth affected by decay or fracture. After taking a high-precision impression of the tooth to be restored, the inlay is manufactured in the dental technician’s lab and then bonded onto the tooth itself by the dentist.
The main clinical uses of inlays are decay treatment, replacement of old fillings which might be worn down or have infiltrations, and various types of tooth fractures.
Inlays are usually used for single reconstructions, which might involve several but not contiguous tooth elements of the same mouth.
Bridges are dental restorations anchored to at least two teeth and they enable the replacement of one or more missing teeth.
The extent of the restoration may vary from a minimum of three teeth (two abutment teeth + one missing tooth) to the whole dental arch. Yet, the correct proportion between the abutment teeth and the teeth to be replaced must always be carefully considered.
If the surface of the tooth is too small, the abutment tooth must be reconstructed with an individualised metal post and core or radicular fiberglass or carbon and composite posts.
The most common material used for the fabrication of bridges is metal-ceramic, but gold can also be used in combination with composite resin or zirconia-ceramic.
Removable prostheses enable the replacement of one or more teeth by means of prostheses that are not permanently fixed inside the mouth but can be anchored to the teeth by means of hooks or connectors.
These prostheses must be removed by the patient every day in order to be cleaned.
Removable partial dentures comprise a metal part, a resin part as well as pre-formed teeth made of resin or ceramic.
Complete dentures are entirely made of resin and the teeth can be made of resin or ceramic.
Removable prostheses are in direct contact with the gums of the dental arches and the gums undergo constant transformations. This is why the internal part of removable prostheses resting on the gums must be periodically reworked (i.e. relined) to ensure the highest level of stability.
If all the teeth are missing, removable prostheses can be anchored to implants, increasing their stability and comfort.
Again, if all the teeth are missing but there is a suitable amount of residual bone tissue, it is possible, with the appropriate number of implants, to restore both dental arches by means of fixed prosthetic devices.